- Tinnitus in one ear is a symptom, not a disease, and it can signal anything from harmless earwax buildup to serious nerve or vascular issues.
- Earwax impaction, infections, and sinus problems are among the most common and easily treatable causes of tinnitus in one ear only.
- Hearing loss, noise exposure, and TMJ disorders can all trigger or worsen one-sided tinnitus due to their effects on ear and nerve function.
- Pulsatile tinnitus—a rhythmic sound matching your heartbeat—may be linked to blood flow or vascular problems and should be evaluated promptly.
- Though rare, tumors like acoustic neuroma can cause tinnitus in one ear only and require medical imaging for diagnosis.
- Early diagnosis is key—sudden hearing loss, dizziness, or tinnitus that affects one ear should be checked by an ENT specialist immediately.
- While not always curable, treating underlying conditions and using management strategies such as sound therapy or CBT can greatly improve quality of life.
If you’ve ever noticed a persistent ringing, buzzing, or whooshing sound in just one ear, you’re not alone. Tinnitus—especially when it affects one ear only—can be confusing and even a little alarming. The causes of tinnitus in one ear only can range from something simple, like a buildup of earwax, to more serious conditions involving nerves, blood flow, or even tumors.
Understanding what’s behind that one-sided ringing is crucial. In this article, we’ll explore the wide range of medical causes of tinnitus in one ear only, how doctors diagnose it, and what treatments may help silence the noise.
What Is Tinnitus and Why Does It Happen?
Tinnitus isn’t a disease by itself—it’s a symptom. It means you’re hearing a sound that doesn’t come from an external source. People describe tinnitus differently: it can sound like ringing, buzzing, humming, clicking, or roaring.
Tinnitus can affect both ears (bilateral) or just one ear (unilateral). When it’s limited to one ear, it’s important to investigate further, because tinnitus in one ear only can sometimes point to specific medical problems that need attention.
How Common Is Tinnitus in One Ear Only?
Tinnitus affects roughly 15% of the population at some point in their lives. However, tinnitus in one ear only is less common than bilateral tinnitus.
Doctors take unilateral tinnitus seriously because it may be linked to conditions that affect only one side of the head or inner ear—like infections, structural problems, or nerve issues. While many cases are benign, it’s worth understanding the possible causes.
Is Earwax One of the Most Common Causes of Tinnitus in One Ear Only?
Yes—earwax is one of the most common and least serious causes. A buildup of earwax, also called cerumen impaction, can block the ear canal and interfere with normal sound transmission.
When this happens, the brain may misinterpret the lack of sound as internal noise, leading to ringing or buzzing in the affected ear.
Symptoms of earwax-related tinnitus:
- Muffled hearing in one ear
- Fullness or pressure sensation
- Itching or discomfort in the ear canal
- Hearing a faint ringing or buzzing that improves after wax removal
Treatment options:
- Over-the-counter ear drops to soften wax
- Professional ear irrigation by a healthcare provider
- Avoiding cotton swabs, which can push wax deeper
If your tinnitus disappears after wax removal, that’s a clear sign it was caused by blockage.
Could an Ear Infection Be the Cause?
Ear infections are another common culprit. When the middle or inner ear becomes inflamed, fluid buildup and pressure can affect hearing and cause tinnitus.
Types of ear infections that may cause tinnitus in one ear:
- Otitis externa (outer ear infection) – often linked to swimming or moisture
- Otitis media (middle ear infection) – typically follows a cold or sinus infection
- Labyrinthitis or vestibular neuritis (inner ear infection) – caused by viruses that affect balance and hearing
These infections can irritate the auditory nerves, producing ringing or buzzing. Once the infection clears, the tinnitus often improves.
What If It’s Due to Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of your throat, helping equalize pressure. When it doesn’t open or close properly—due to allergies, sinus problems, or infections—it can create pressure changes that distort hearing.
This dysfunction can cause sensations of fullness, popping, and sometimes tinnitus in one ear only.
Common triggers include:
- Allergies or colds
- Altitude or air pressure changes
- Chronic sinus issues
Treating the underlying sinus or allergy problem often relieves the tinnitus.
Can Sinus Problems or Nasal Congestion Lead to Tinnitus?

Absolutely. Nasal congestion can affect ear pressure, especially when the sinuses and Eustachian tubes become blocked. The trapped pressure alters sound transmission and can cause temporary tinnitus.
If your tinnitus appears alongside nasal stuffiness, postnasal drip, or facial pressure, sinus issues could be the reason.
How Does Hearing Loss Connect to Tinnitus in One Ear?
Hearing loss and tinnitus often go hand in hand. When the auditory system loses sensitivity to certain sound frequencies, the brain compensates by generating its own noise—tinnitus.
Unilateral hearing loss (hearing loss in one ear) may result from:
- Noise exposure (like concerts or power tools)
- Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (a medical emergency)
- Aging-related damage (presbycusis)
- Ear trauma
If you notice sudden hearing loss in one ear along with tinnitus, see an ear specialist immediately. Quick treatment can improve your chances of recovery.
Could Noise Exposure Affect Just One Ear?
Yes, it can. If you’re frequently exposed to loud sounds on one side—such as shooting firearms, using power tools, or wearing headphones unevenly—you might develop tinnitus in one ear only.
Preventive measures:
- Always wear hearing protection in noisy environments
- Avoid prolonged use of earbuds or headphones at high volume
- Alternate sides when using devices close to the ear
Noise-induced tinnitus can be permanent if the damage is severe, so prevention is key.
Is It Possible That Jaw Problems Are Involved?
Surprisingly, yes. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is located near the ear, and problems with jaw alignment or muscle tension can affect nearby nerves and cause tinnitus.
Signs your tinnitus may be TMJ-related:
- Jaw clicking or popping
- Pain when chewing or yawning
- Tinnitus that worsens when moving the jaw
Treatment might include physical therapy, bite correction, or stress reduction.
Can Tinnitus in One Ear Be Caused by Blood Flow Problems?
Sometimes the cause is pulsatile tinnitus—a rhythmic sound that matches your heartbeat. This type of tinnitus often stems from issues with blood flow near the ear.
Possible vascular causes include:
- Atherosclerosis (narrowed arteries)
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal blood vessels (like arteriovenous malformations)
- Benign intracranial hypertension (increased brain pressure)
Unlike standard tinnitus, pulsatile tinnitus is usually objective—sometimes even audible to a doctor during an exam.
Because it can be linked to vascular issues, it’s important to have this type evaluated promptly.
Could Tinnitus in One Ear Indicate a Tumor?
While rare, one of the more serious causes of tinnitus in one ear only is a tumor on the hearing or balance nerve, known as an acoustic neuroma (or vestibular schwannoma).
This noncancerous tumor grows slowly on the nerve that connects the inner ear to the brain. As it enlarges, it can press on surrounding structures, causing:
- Tinnitus in one ear only
- Gradual hearing loss
- Balance problems or dizziness
- Facial numbness or tingling
Doctors typically diagnose it using MRI scans. Treatment options depend on tumor size and symptoms and may include monitoring, surgery, or radiation therapy.
What About Ear or Head Trauma?
Injuries can also lead to tinnitus in one ear only. A blow to the head or direct ear trauma can damage inner ear structures, cause bleeding, or affect the auditory nerve.
If your tinnitus began after an accident, fall, or loud explosion, it’s important to seek a medical evaluation. In some cases, fluid leaks or nerve damage may need urgent care.
Can Medications Trigger One-Sided Tinnitus?
Certain medications—known as ototoxic drugs—can damage the ear’s sensory cells, leading to hearing changes and tinnitus. Although most cases affect both ears, sometimes one ear is more sensitive.
Common ototoxic medications include:
- High doses of aspirin or NSAIDs
- Certain antibiotics (like gentamicin)
- Chemotherapy drugs (like cisplatin)
- Loop diuretics for high blood pressure
Never stop medication on your own, but if tinnitus appears while taking new medicine, discuss alternatives with your doctor.
Are Nerve-Related Disorders to Blame?
The auditory nerve transmits sound information to the brain. When something disrupts this pathway—such as inflammation, compression, or demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis—tinnitus can develop in one ear.
Signs it might be nerve-related:
- Tingling or weakness in nearby areas
- Vision or coordination issues
- Tinnitus that coincides with neurological symptoms
In such cases, imaging tests like MRI help confirm the cause.
How Do Doctors Diagnose the Causes of Tinnitus in One Ear Only?
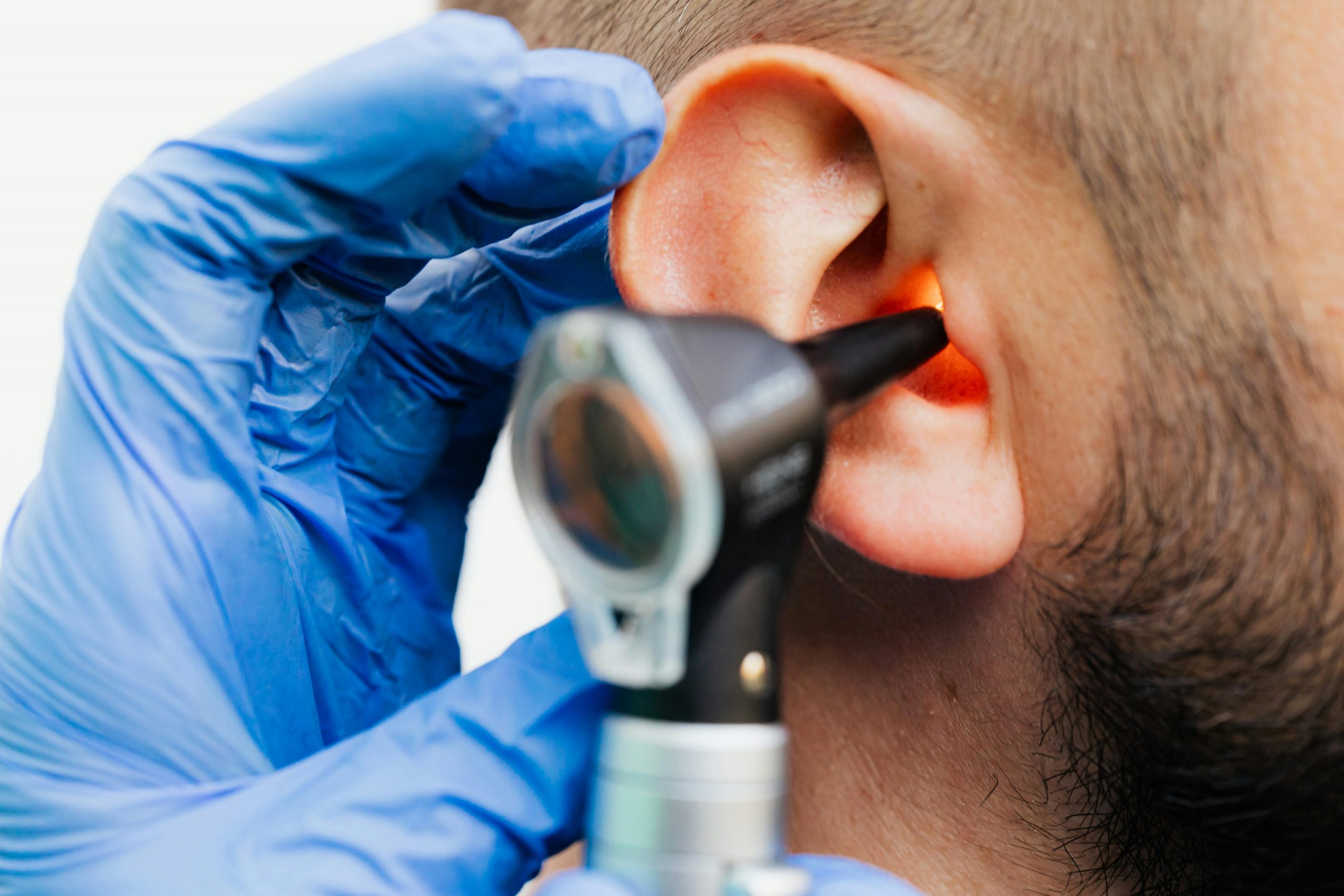
Diagnosis often starts with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Doctors ask questions about:
- Duration and type of tinnitus sound
- Associated hearing loss or dizziness
- Recent illnesses, injuries, or medication use
Common diagnostic tests include:
- Hearing tests (audiometry) – to assess any hearing loss pattern
- Otoscopy – to look for earwax or infection
- Tympanometry – to check middle ear pressure
- Imaging (MRI or CT scans) – to detect tumors, structural issues, or vascular abnormalities
If the tinnitus has a pulsating rhythm, doctors may use specialized scans to assess blood flow near the ear.
When Should You Worry About Tinnitus in One Ear?
Not every ringing sound is serious, but certain symptoms deserve prompt attention.
See a doctor right away if you notice:
- Sudden hearing loss in one ear
- Tinnitus accompanied by dizziness or imbalance
- Tinnitus that pulsates with your heartbeat
- Ear pain, drainage, or facial weakness
Early evaluation can help rule out major problems and prevent complications.
How Are the Medical Causes of Tinnitus in One Ear Only Treated?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. The goal is to fix the problem when possible or manage the tinnitus if it’s permanent.
Treatment approaches include:
- Treating the underlying condition
- Removing impacted earwax
- Prescribing antibiotics for infection
- Adjusting medications if ototoxicity is suspected
- Managing blood pressure or vascular health
- Restoring hearing
- Hearing aids for hearing loss
- Cochlear implants in severe cases
- Managing symptoms
- Sound therapy (white noise machines or apps)
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Relaxation techniques and stress management
- Medical or surgical intervention
- Surgery for tumors or structural problems
- Specialized care for TMJ or sinus disorders
Can You Prevent Tinnitus in One Ear?
While not every case is preventable, you can reduce your risk significantly by protecting your ears and maintaining overall health.
Preventive tips:
- Limit exposure to loud noises
- Use ear protection at concerts or workplaces
- Avoid inserting objects into the ear canal
- Manage allergies and sinus infections early
- Keep blood pressure and cholesterol in check
- Avoid excessive use of ototoxic medications
Healthy lifestyle habits can make a big difference in maintaining hearing health.
What If the Ringing Doesn’t Go Away?
Sometimes tinnitus lingers even after treating the main cause. In such cases, doctors focus on management strategies to help you adapt.
Helpful approaches include:
- Sound therapy: Using background sounds to mask tinnitus
- Hearing aids: Improving sound input can reduce perception of tinnitus
- CBT or mindfulness: Reduces stress and helps reframe how you perceive tinnitus
- Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT): Combines sound and counseling to “train” the brain to ignore the noise
While there’s no one-size-fits-all cure, most people find ways to manage their symptoms effectively.
What’s the Outlook for People with Tinnitus in One Ear Only?
The outlook depends on the cause.
- If it’s due to earwax, infections, or sinus issues, tinnitus often disappears after treatment.
- When related to hearing loss or nerve problems, it may persist but can usually be managed.
- If caused by tumors or vascular issues, proper diagnosis and medical care can prevent progression and restore function.
The key is getting evaluated early and not ignoring persistent symptoms.
When to See an ENT Specialist
If tinnitus lasts more than a few weeks or affects only one ear, schedule an appointment with an ENT (ear, nose, and throat specialist). These professionals can perform the detailed exams and tests needed to pinpoint the exact cause.
They may also refer you to:
- An audiologist for hearing evaluation
- A neurologist if nerve problems are suspected
- A vascular specialist for pulsatile tinnitus
Getting the right specialist involved ensures faster answers and better outcomes.
The Bottom Line
Tinnitus in one ear only can be caused by a wide range of medical conditions—from something as simple as earwax buildup to more serious issues like tumors or nerve disorders. While it can be unsettling, many causes are treatable once identified.
If you notice persistent ringing, buzzing, or pulsing sounds in one ear, don’t ignore them. See your doctor or an ENT specialist for a proper diagnosis. The sooner you identify the underlying problem, the better your chances of finding relief.
Understanding the medical causes of tinnitus in one ear only is the first step toward restoring your peace and quiet.

